Colorless diamonds: The rarest and highest quality with a pure icy look.
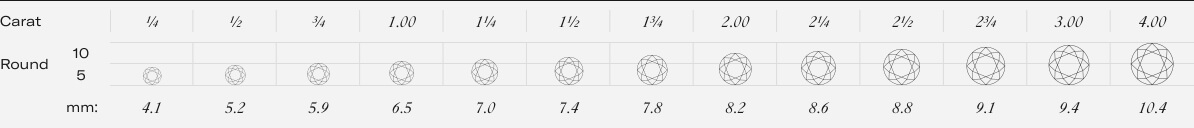
Carat
Diamond weight is measured in carats. 1 carat = 200 mg = 0.2 grams. One carat is divided into one hundred parts, and each part is called a point. 0.75 carat (3/4 carat) is also known as 75 points, and 0.01 carat is 1 point. Under other similar conditions, as the weight of the diamond increases, its value increases exponentially. If you want to pursue the size of 1 carat but feel that the price is too expensive, you may wish to choose a loose diamond with a score of 90 or more. The visual difference is the same, but the price will be much lower.
Round
Princess
Cushion
Emerald
Asscher
Oval
Pear
Marquise
Heart
TIPS: How to choose carat weight
It is very important to measure the budget before buying a diamond. The following are suggestions for you to choose the size of the diamond:
- Refer to the budget for most people to choose a diamond, which is about "one to two months' salary", which is worth investing for her.
- Assuming that the one-carat diamond ring you want to buy exceeds your budget, you can slightly lower the standards in terms of color (color), clarity (clarity), and cut (cut), and you can still choose a beautiful diamond that meets her needs.
- Please pay attention to the slenderness of your other half of the finger. If the one-carat diamond ring does not match her hand shape, you can consider the weight of less than one carat.
- Diamonds of the same size are placed on various styles and settings, and the visual effects will be different. Please use your creativity to choose an exclusive diamond ring for her.
Color
Diamonds come in a variety of natural colors, ranging from precious colorless to rare light blue and pink to common yellowish. The more transparent and colorless it is, the easier it is for light to penetrate, and the more colorful it is after refraction and dispersion. Diamond color grading is determined by technicians repeatedly comparing diamonds to be graded with standard color master stones in a professional laboratory grading environment. Colorless diamonds are graded D (that is, starting from the first letter of Diamond). The closer a diamond is to pure colorless, the better it is. Diamond color evaluation and classification is based on the standards established by GIA, from D (high-quality colorless) to Z (pale yellow or brown) in alphabetical order, divided into 23 grades.
-
DEF
-
GHIJ
Near-colorless diamonds: No discernible color; great value for the quality.
-
KLM
Faint color diamonds: Budget-friendly pick; pairs beautifully with yellow gold.
-
NOP
Slightly yellow level, the color can be seen with the naked eye.
Clarity
Diamonds are crystallized in the mantle magma deep in the earth. The environment is complex, the composition is diverse, and the temperature and pressure are extremely high. After hundreds of millions of years of geological changes, it is inevitable to contain various impurities or flaws inside. The color, number, size, and location distribution of these inclusions have different degrees of influence on the clarity of the diamond. Every diamond contains natural inclusions, like natural birthmarks. As the name suggests, inclusions are hidden within the diamond, and they can come in different colors: white, black, colorless, or even green or red. Most of the inclusions cannot be identified with the naked eye, and must be clearly seen under a 10x magnifying glass.
-
FL
Flawless diamonds are the highest quality in GIA diamond grading. No inclusions can be seen under 10x magnification.
-
IF
Internally flawless, it is also a very beautiful and rare diamond, and only tiny, almost invisible surface feature inclusions can be seen with a 10x magnifying glass.
-
VVS1-VVS2
Contains very slight inclusions that require careful attention even under 10x magnification.
-
VS1-VS2
Contains a small amount of inclusions that can only be seen with a 10x magnifying glass and are not visible to the naked eye.
-
SI1-SI2
Inclusions can be seen under 10x magnification, visible to the naked eye but not obvious.
-
I1-I3
Obvious blemishes, only suitable for accessories.
Cut
Diamond cutting mainly includes three aspects of diamond cutting, polishing and symmetry. A good cut should reflect the brightness and fire of the diamond as much as possible, and try to keep the weight of the original stone as much as possible. The cutting grades of IGI International Gemological Institute are divided into ID (), EX (excellent), VG (very good) and G (good) from high to low. The Chinese national inspection is divided into VG (very good) and G (good). The cut of a diamond is the most important of the 4Cs. It is the only important factor that allows the beauty of diamonds to be further enhanced by the operation of technicians. So diamond cut can also be said to be the "second life" of diamonds. This manual standard depends on the talent and experience of the diamond cutter.
-
IDEAL
Eight hearts and eight arrows cut, this kind of cut makes the diamond reflect almost all the light entering the diamond, only 0 in the world. 15% diamonds belong to this cutter.
-
EX
The cut represents a standard that only 3% of first-class high-quality diamonds can meet. This cut makes the diamond reflect almost all the light entering the diamond.
-
VG
VERY GOOD, which represents about 15% of diamond cutters, can make diamonds reflect the light of standard-grade cutters.
-
GD
A good cutter does not affect the beauty and fire color of the diamond, but the reflected light is far less than that of VG cutter.
-
FAIR
Poor cutting, which includes all diamonds that do not meet the general cutting standards. The cutting of these diamonds is either deep and narrow or shallow and wide for light to overflow from the edge or bottom.
